Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Impulse predictors for epochs
epoch_impulse_predictor() generates predictor variables for reverse
correlation in trial-based experiments with discrete events. The function
generates one impulse per trial, and these impulsescan be of varaiable magnitude
and have variable latency.
The example uses simulated data meant to vaguely resemble data from an N400 experiment, but not intended as a physiologically realistic simulation.
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
from eelbrain import *
ds = datasets.simulate_erp(snr=1)
print(ds.summary())
Key Type Values
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
eeg NDVar 140 time, 65 sensor; -8.21333e-06 - 8.36563e-06
cloze Var 0.00563694 - 0.997675
predictability Factor high:40, low:40
n_chars Var 3:10, 4:20, 5:22, 6:16, 7:12
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dataset: 80 cases
Discrete events
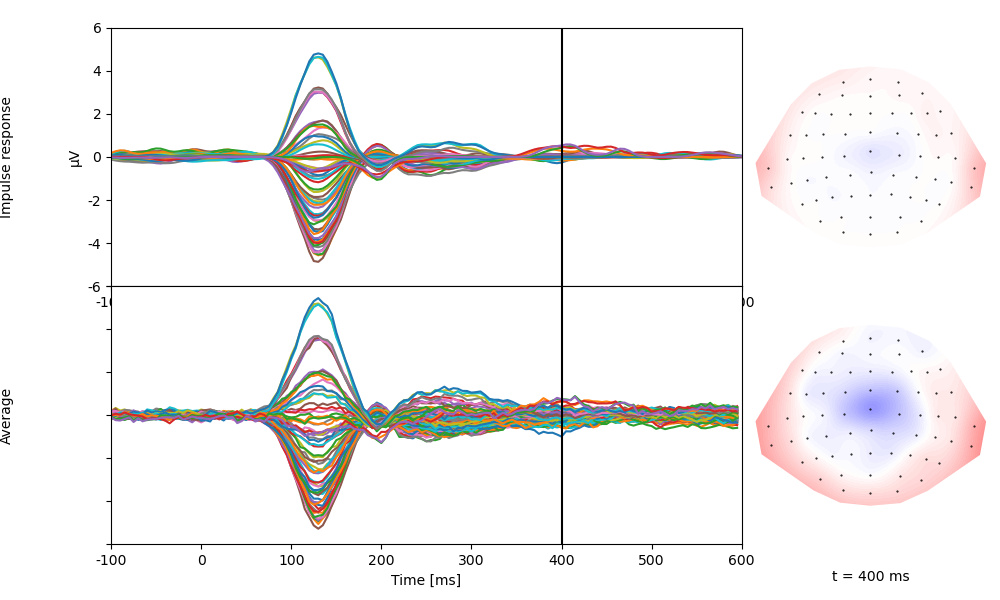
Computing a TRF for an impulse at trial onset is very similar to averaging:
any_trial = epoch_impulse_predictor('eeg', 1, data=ds)
fit = boosting('eeg', any_trial, -0.100, 0.600, basis=0.050, data=ds, partitions=2, delta=0.01)
average = ds['eeg'].mean('case')
trf = fit.h.sub(time=(average.time.tmin, average.time.tstop))
p = plot.TopoButterfly([fit.h_scaled, average], xlim=(-0.100, 0.600), axtitle=['Impulse response', 'Average'], t=0.400)
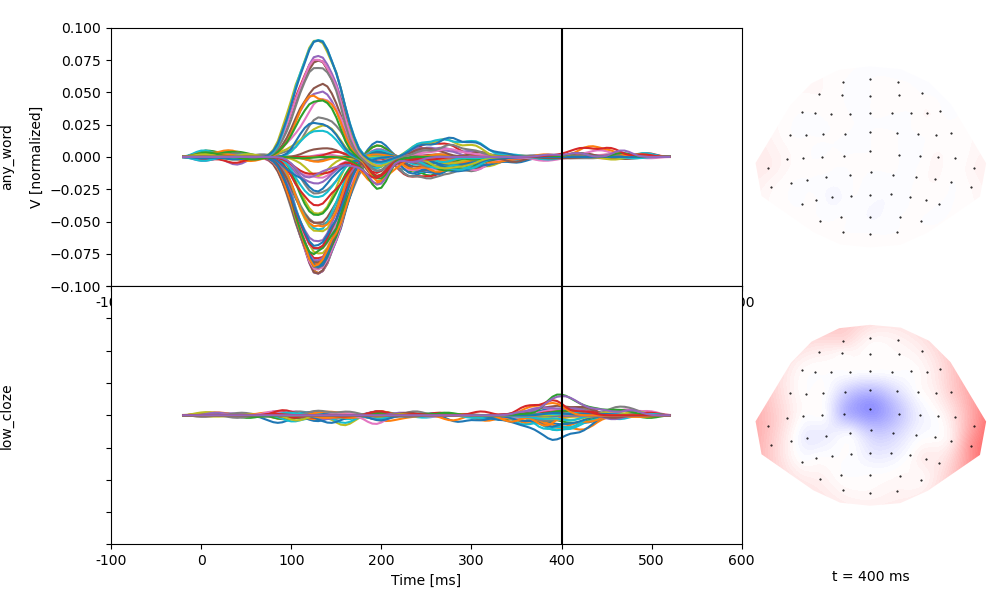
Categorial coding
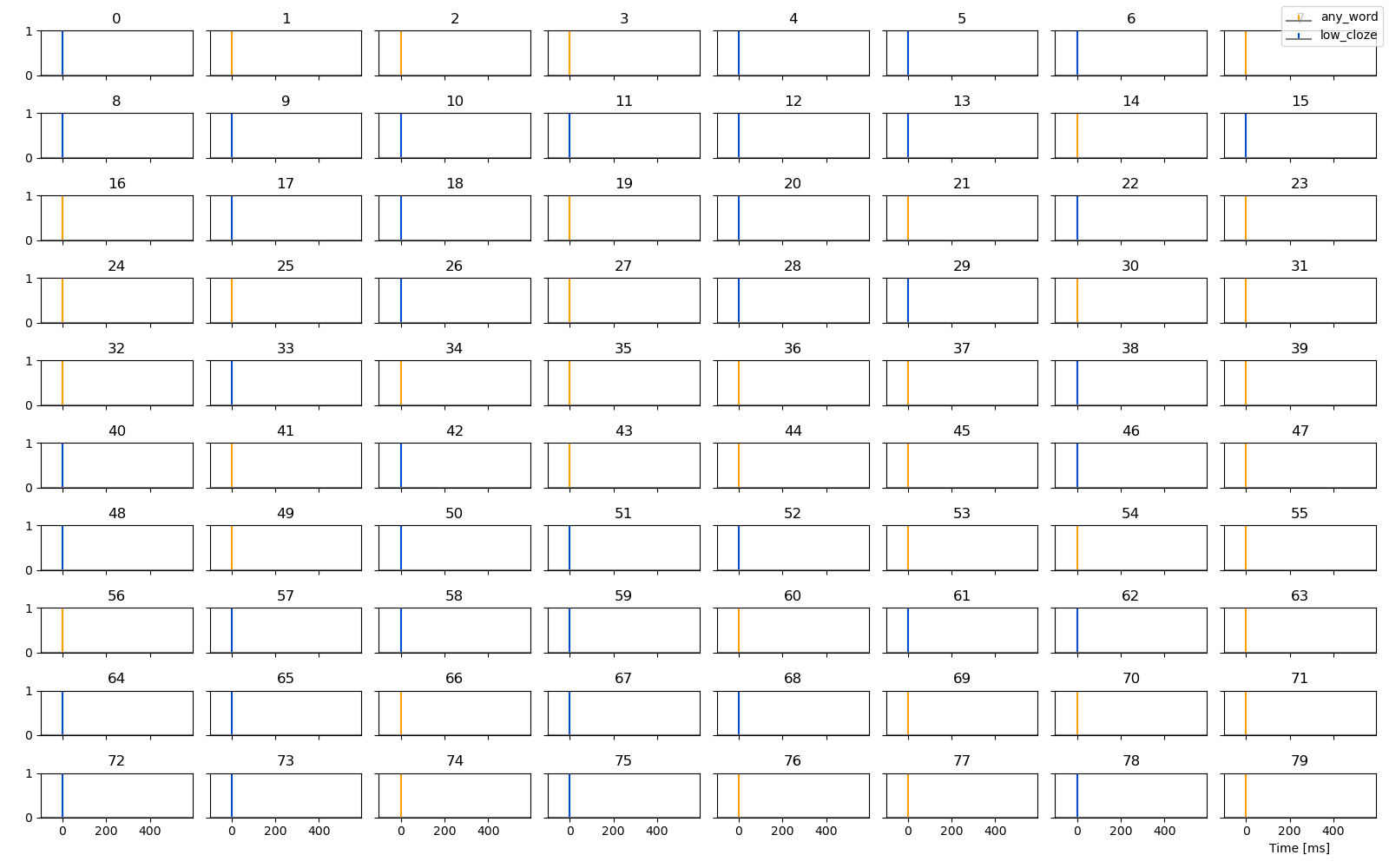
Impulse predictors can be used like dummy codes in a regression model.
Use one impulse to code for occurrence of any word (any_word), and a
second impulse to code for unpredictable words only (cloze):
any_word = epoch_impulse_predictor('eeg', 1, data=ds, name='any_word')
# effect code for cloze (1 for low cloze, -1 for high cloze)
cloze_code = Var.from_dict(ds['predictability'], {'high': 0, 'low': 1})
low_cloze = epoch_impulse_predictor('eeg', cloze_code, data=ds, name='low_cloze')
# plot the predictors for each trial
p = plot.UTS([any_word, low_cloze], '.case', stem=True)

Estimate response functions for these two predictors. Based on the coding,
any_word reflects the response to predictable words, and low_cloze
reflects how unpredictable words differ from predictable words:
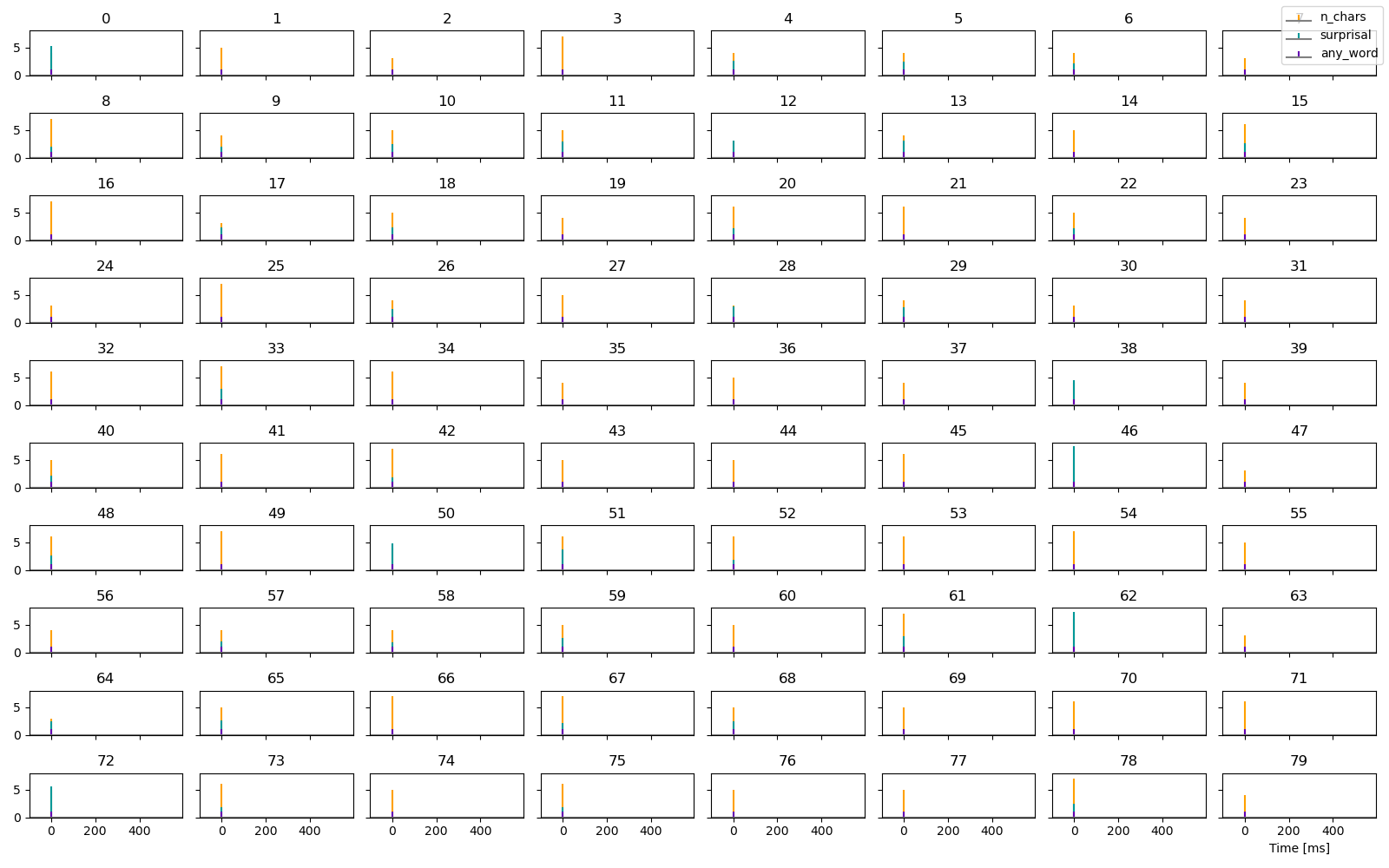
Continuous coding
Impulse predictors can similarly accommodate continuous variables:
# effect code for cloze (1 for low cloze, -1 for high cloze)
n_chars = epoch_impulse_predictor('eeg', 'n_chars', data=ds, name='n_chars')
surprisal = epoch_impulse_predictor('eeg', '-numpy.log2(cloze)', data=ds, name='surprisal')
# plot the predictors for each trial
p = plot.UTS([n_chars, surprisal, any_word], '.case', stem=True)
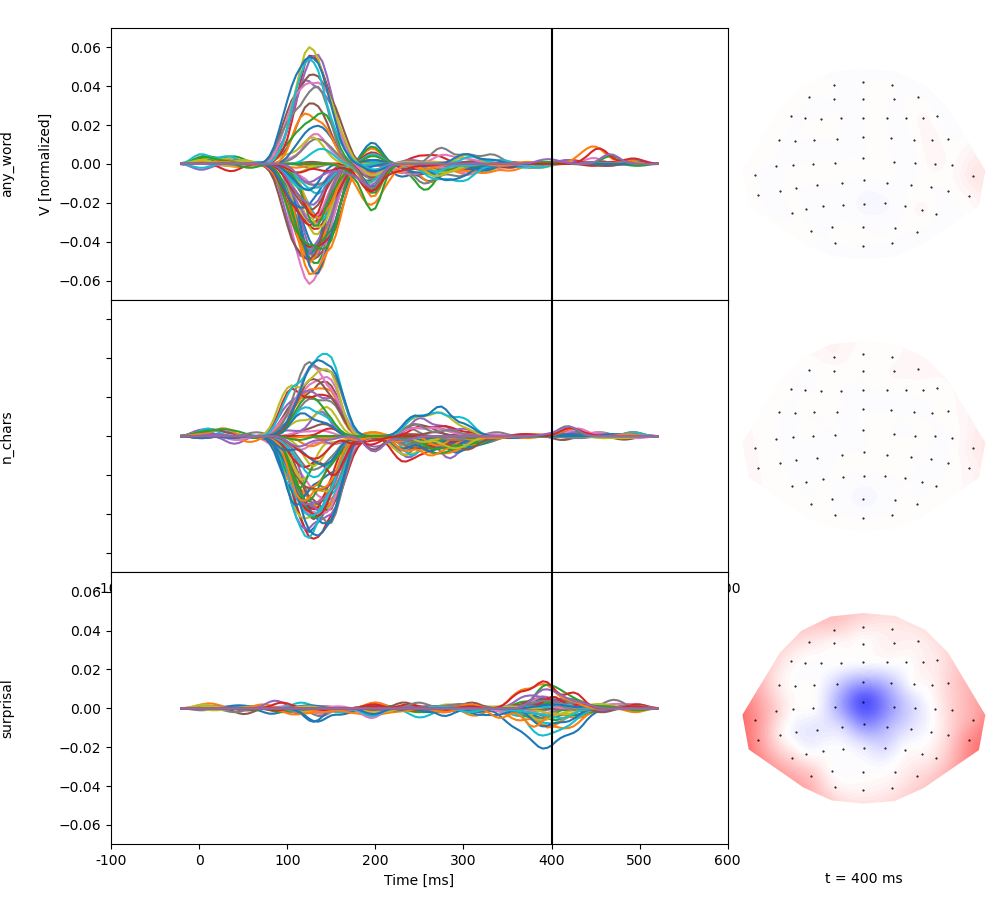
Estimate response functions. Based on the coding, any_word reflects the
hypothetical response to a words with 0 characters and 0 surprisal, whereas
the two other predictors reflect the change in response by n_chars and
surprisal:
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 2.815 seconds)